Vancomycin is a narrow-spectrum antibiotic used to treat infections caused by specific bacteria. It is not effective against all types of bacteria, making it a narrow-spectrum antibiotic.
Unlike broad-spectrum antibiotics, vancomycin targets a specific group of bacteria and is commonly used to treat serious infections such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Clostridium difficile. Vancomycin, a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, is specifically designed to target a select group of bacteria rather than a wide range.
This makes it a crucial medication for treating specific, serious bacterial infections. Understanding the spectrum of an antibiotic is essential for doctors and healthcare providers to ensure the most effective treatment for patients. We will explore the characteristics and applications of vancomycin, shedding light on its narrow-spectrum antibiotic properties and the significance of its targeted approach in combating bacterial infections.
Vancomycin Antibiotic Spectrum Explained
In the world of antibiotics, the term “spectrum” refers to the range of bacteria that a particular antibiotic is effective against. Each antibiotic has a specific spectrum, which can be categorized as either broad-spectrum or narrow-spectrum. When it comes to vancomycin, it falls under the category of a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, meaning it is effective against a limited range of bacteria.
Definition Of Antibiotic Spectrum
The antibiotic spectrum refers to the range of bacteria that a specific antibiotic can target and kill. It is a crucial factor in determining the appropriate use of an antibiotic for treating bacterial infections.
Vancomycin’s Place In The Spectrum
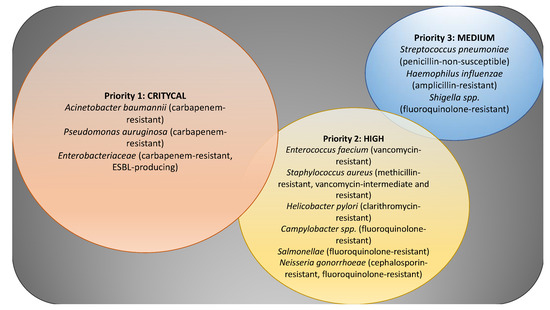
Vancomycin is classified as a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, primarily targeting gram-positive bacteria. This includes bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, and Clostridium difficile. It is not effective against gram-negative bacteria, making it important to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection before prescribing vancomycin.
Classifying Vancomycin’s Spectrum
Vancomycin is commonly known as a potent antibiotic used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Understanding whether it falls under the category of broad or narrow spectrum antibiotics is crucial for its appropriate use in clinical practice.
The Concept Of Broad-spectrum Antibiotics
Broad-spectrum antibiotics are designed to target a wide range of bacteria, including both gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. They are effective against a diverse array of bacterial species, making them valuable in treating infections when the specific pathogen is unknown.
The Concept Of Narrow-spectrum Antibiotics
Narrow-spectrum antibiotics, on the other hand, are selective in their action and only target a specific group of bacteria. They are effective against either gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria, but not both, and are usually prescribed when the infecting organism has been identified.
Criteria For Classification
Classifying an antibiotic as broad or narrow spectrum depends on its ability to target a broad or specific range of bacteria. The key factors influencing this classification include the antibiotic’s mechanism of action, the spectrum of activity (broad or narrow), and the specific bacterial species it targets.
Vancomycin’s Mechanism Of Action
How Vancomycin Fights Bacteria
Vancomycin, primarily a bactericidal antibiotic, works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. It targets the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a major component of the bacterial cell wall, by binding to the D-Ala-D-Ala terminus of peptidoglycan precursors. This binding prevents the cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains, leading to the disruption of bacterial cell wall formation and eventual lysis of the bacterial cell.
Its Impact On Bacterial Populations
Vancomycin’s mechanism of action is specifically focused on Gram-positive bacteria, making it a narrow-spectrum antibiotic. It does not affect Gram-negative bacteria due to the differences in their cell wall structure. The targeted action of vancomycin ensures that it has a selective impact on bacterial populations, effectively eradicating certain infections caused by susceptible bacteria while sparing the beneficial bacteria present in the body.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Vancomycin’s Target Bacteria
Vancomycin is an essential antibiotic used to treat severe bacterial infections. Understanding the specific types of bacteria vancomycin targets provides invaluable insight into its effectiveness in clinical use.
Types Of Bacteria Susceptible To Vancomycin
Vancomycin primarily targets Gram-positive bacteria, making it a powerful tool in fighting infections caused by this group of organisms. It is especially effective against bacteria such as:
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
- Streptococci
- Enterococci
Comparison To Other Antibiotics’ Target Range
When compared to other antibiotics, vancomycin’s spectrum is relatively narrow, as it predominantly targets Gram-positive bacteria. In contrast, broad-spectrum antibiotics have a wider range of activity, capable of targeting both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Clinical Uses Of Vancomycin
Vancomycin is a powerful antibiotic widely used in clinical settings to combat bacterial infections. Understanding its clinical uses is crucial in optimizing patient care and treatment outcomes. Let’s delve into the vital role of vancomycin in treating infections and instances where it is the preferred choice.
Vancomycin’s Role In Treating Infections
Vancomycin is primarily used to treat infections caused by gram-positive bacteria, particularly those resistant to other antibiotics. These include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Clostridium difficile, which are notorious for causing severe and sometimes life-threatening infections.
Instances Where Vancomycin Is The Preferred Choice
Vancomycin is often the preferred choice in cases where the causative organism is known or suspected to be resistant to other antibiotics, such as penicillin or cephalosporins. It is also commonly employed in patients with a severe penicillin allergy or those unable to tolerate other antibiotics. Moreover, vancomycin is frequently used in surgical prophylaxis to prevent infections, particularly in procedures involving implantation of prosthetic devices.
Is Vancomycin Broad Or Narrow Spectrum: Unraveling Its Antibiotic Reach
Is Vancomycin Broad Or Narrow Spectrum: Unraveling Its Antibiotic Reach
Analyzing The Antibiotic Reach Of Vancomycin
Vancomycin, a potent antibiotic used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, is classified as a broad-spectrum antibiotic. It effectively targets a wide range of gram-positive bacteria, including strains resistant to other antibiotics. This broad spectrum of activity makes vancomycin an invaluable tool in combating severe infections caused by organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis. The distinct mechanism of action of vancomycin, which disrupts bacterial cell wall synthesis, contributes to its efficacy against a diverse array of pathogens, making it a pivotal component of the antibiotic armamentarium.
Impact Of Its Reach In Clinical Decision-making
The broad-spectrum nature of vancomycin significantly influences clinical decision-making, especially in cases where empirical therapy is necessary. Its extensive coverage makes it a viable choice in treating infections when the causative organism is unidentified or when infections involve multiple potential pathogens. Despite its broad reach, it’s essential to employ vancomycin judiciously to prevent the emergence of resistant strains and reduce the risk of adverse effects. With careful consideration of its antibiotic reach, healthcare providers can optimize the use of vancomycin to achieve favorable clinical outcomes while minimizing the development of resistance.
Resistance And Implications For Vancomycin
Vancomycin, a potent antibiotic often considered a last resort for treating serious bacterial infections, has historically been highly effective. However, the emergence of antibiotic resistance presents a significant threat to its efficacy. Understanding the implications of resistance and the future outlook for Vancomycin is critical in combating bacterial infections.
The Issue Of Antibiotic Resistance
The rise of antibiotic resistance is a global concern, impacting the effectiveness of many antibiotics, including Vancomycin. Bacteria can develop resistance to antibiotics through various mechanisms, such as genetic mutations or the acquisition of resistance genes. Vancomycin-resistant bacteria pose a particularly alarming challenge, as they limit treatment options for life-threatening infections, leading to higher morbidity and mortality rates.
Future Outlook For Vancomycin’s Efficacy
In response to the growing resistance, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing Vancomycin’s efficacy and combating resistance. Scientists are exploring novel formulations and delivery methods to improve the drug’s penetration into bacterial cells and overcome resistance mechanisms. Additionally, combination therapies and synergistic approaches are being investigated to potentiate Vancomycin’s activity against resistant bacteria. The development of new antibiotics and alternative treatment strategies also plays a crucial role in safeguarding Vancomycin’s effectiveness in the face of resistance.
Frequently Asked Questions Of Is Vancomycin Broad Or Narrow Spectrum
Is Vancomycin A Broad Spectrum Antibiotic?
Vancomycin is considered a narrow-spectrum antibiotic that primarily targets gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species. It is not effective against gram-negative bacteria.
Can Vancomycin Treat Mrsa Infections?
Yes, Vancomycin is often used as a first-line treatment for MRSA (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus) infections, making it a crucial medication for combating these resistant strains of bacteria.
What Are The Common Side Effects Of Vancomycin?
Common side effects of Vancomycin may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and kidney problems. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience severe side effects while taking Vancomycin.
Conclusion
Vancomycin’s broad spectrum makes it effective against a variety of bacteria. However, its overuse can lead to resistance. Understanding its spectrum can help ensure appropriate use and avoid unnecessary risks. Keep in mind the importance of expert guidance for optimal treatment outcomes.
