Yes, Vancomycin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. It is effective against several types of bacteria, including many Gram-positive strains.
Vancomycin stands out as a powerful weapon in the medical arsenal against severe bacterial infections, particularly those resistant to other antibiotics. Its broad-spectrum activity is especially valuable in treating complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, and pneumonia. Due to its potency, healthcare professionals often reserve vancomycin for cases where other antibiotics have failed or when the patient has allergies to alternative medications.
As resistance to antibiotics continues to challenge healthcare, vancomycin’s role has become crucial in the fight against resistant strains like MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). Its use, however, is closely monitored to prevent further resistance development and protect its efficacy for serious infections.
Vancomycin Explained
Understanding the world of antibiotics can be complex, but Vancomycin stands out as a powerful ally in the fight against bacterial infections. Known for its potency and broad-spectrum capabilities, Vancomycin has played a crucial role in healthcare. In this in-depth look, we explore what Vancomycin is, its important characteristics, and a brief history, providing insights into why it remains a cornerstone in antimicrobial treatments.
What Is Vancomycin?
Vancomycin is an antibiotic medication noted for its effectiveness against a range of bacterial infections. Primarily, its utilization targets severe cases and infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria, including MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). Administered intravenously or orally, depending on the infection site, Vancomycin stands as a critical drug in instances where other antibiotics may fail.
Important Characteristics
- Spectrum: Vancomycin is classified as a broad-spectrum antibiotic owing to its efficacy against various bacterial strains.
- Mode of Action: It works by inhibiting cell wall synthesis in bacteria, which is vital for their survival and multiplication.
- Resistance: While powerful, the emergence of Vancomycin-resistant bacteria has become a concern, necessitating judicious use.
- Administration: The delivery method of Vancomycin is critical and tailored to the infection, be it intravenous for systemic infections or oral for gastrointestinal conditions like Clostridium difficile.
- Side Effects: Physicians monitor patients closely as it can cause side effects such as ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity.
The History Of Vancomycin
The journey of Vancomycin began in the early 1950s, when it was discovered in a laboratory from soil samples. The antibiotic was isolated from the bacterium Amycolatopsis orientalis (formerly Streptomyces orientalis). It was not until 1958 that Vancomycin was approved and began its mission to treat complex infections. Decades of utilization have cemented its status as a last-resort antibiotic for infections that are resistant to other treatment options.
Antibiotic Classification
Antibiotics wield the power to combat infections by targeting the bacteria that cause them. These potent medicines are not all the same, though—each one has a specific range of bacteria it combats. The classification of antibiotics into various categories helps in choosing the right kind to effectively treat a particular infection, ensuring that the bacteria present is susceptible to the antibiotic prescribed. Vancomycin, in particular, attracts attention in this expansive realm of antibiotic agents for its distinct characteristics and the range of bacteria it targets.
Classifying antibiotics is an essential process in understanding their mechanism of action, spectrum of activity, and potential side effects. This helps healthcare professionals to prescribe them judiciously, promoting effective treatment and minimizing antibiotic resistance. The spectrum of an antibiotic—whether it’s narrow or broad—dictates which pathogens it can potentially eradicate.
Differences Between Antibiotics
Antibiotics are not a one-size-fits-all solution. They differ based on their chemical structure, mechanism of action, and spectrum of activity. Some antibiotics target the cell walls of bacteria, while others interfere with protein synthesis or DNA replication. The specificity of their action leads to the categorization into bactericidal or bacteriostatic drugs—either killing bacteria or inhibiting its growth, respectively.
Narrow Vs. Broad Spectrum Antibiotics
Narrow spectrum antibiotics are akin to sniper rifles—precise and targeted, best used when the specific bacteria responsible for an infection are known. These drugs are effective against a select group of microorganisms. Broad spectrum antibiotics, on the other hand, resemble a net cast wide in the sea, catching a range of bacterial species without discrimination. They’re particularly useful in situations where the infecting bacteria are unknown, or when treating mixed bacterial infections. However, the broad activity comes with a risk of disturbing natural body flora and promoting antibiotic resistance.
| Antibiotic Type | When to Use | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Narrow Spectrum | Targeted treatment of specific bacteria | Penicillin, Erythromycin |
| Broad Spectrum | Treating a wide range of bacteria or unknown pathogens | Tetracycline, Vancomycin |
Understanding whether Vancomycin falls under the narrow or broad spectrum is critical for healthcare providers. This knowledge helps in selecting the most appropriate antibiotic for treatment while aiming to protect beneficial bacteria and deter the spread of resistance.
Is Vancomycin Broad Spectrum? Unveiling Antibiotic Power
Welcome to the world of antibiotics, where the battle against bacterial infections takes center stage. Among the heavy hitters in this arena is vancomycin, a medication that has sparked curiosity and debate among healthcare professionals and patients alike. Join us as we unravel the mysteries behind vancomycin, starting with a crucial question: Is vancomycin a broad spectrum antibiotic? Prepare to dive deep as we unveil the potent antibiotic power of vancomycin.
Definition Of Broad Spectrum Antibiotics
Broad-spectrum antibiotics are the superheroes of the pharmaceutical world, equipped with the power to target and eliminate a wide range of bacterial adversaries. Unlike their narrow-spectrum counterparts that focus on a select group of pathogens, broad-spectrum antibiotics offer a more inclusive approach, able to tackle numerous strains of bacteria, both gram-positive and gram-negative. This versatility makes them especially valuable in battles where the bacterial villain’s identity remains a mystery.
Vancomycin’s Mechanism Of Action
At its core, vancomycin operates with a straightforward mission: to disrupt the construction of cell walls in bacteria. It’s like putting a halt to the enemy’s fortifications, leaving them vulnerable and ultimately leading to their demise. Vancomycin specifically targets the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall by binding to the D-alanyl-D-alanine terminus of cell wall precursors. This action prevents the incorporation of these precursors into the cell wall, resulting in weakened walls and bacterial cell death.
Spectrum Of Activity Of Vancomycin
Vancomycin’s resume features a list of targeted bacteria skewed significantly towards the gram-positive side. This means its spectrum of activity is more specialized, targeting behemoths like Staphylococcus aureus, including the notorious MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), and its kindred, Streptococcus species. Vancomycin’s effectiveness against Clostridioides difficile makes it a key treatment option for related infections.
| Bacteria Type | Vancomycin Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Gram-positive bacteria | Highly effective |
| Gram-negative bacteria | Limited effectiveness |
| MRSA | Highly effective |
| Clostridioides difficile | Highly effective |
In summary, while vancomycin is indeed a powerful antibiotic, its scope cannot be classified as broadly reaching across the spectrum of bacterial pathogens. Its action is potent, but primarily tailored to the gram-positive contingent.
Indications Of Vancomycin Use
The Indications of Vancomycin Use are notably pointed toward the treatment of severe infections caused by gram-positive bacteria, among which Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin-resistant strains (MRSA), stands as a considerable adversary. Given the resistance concerns posed by such bacterial strains, experts consider Vancomycin a critical arrow in the quiver of antimicrobial defenses. It’s a flagship example of a broad-spectrum antibiotic with a specific focus, proving to be vital for patients where other treatments have failed or are not suitable.
Infections Treated By Vancomycin
Vancomycin is known for its effectiveness against a range of infections, allowing clinicians to address:
- Skin and soft tissue infections: Including those that are complicated or caused by MRSA.
- Bloodstream infections: Particularly those resulting from central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs).
- Bone and joint infections: Such as osteomyelitis or septic arthritis, often occurring post-surgery or from contiguous spread of infection.
- Endocarditis: An infection of the heart valves especially in high-risk patients.
- Pneumonia: Covering hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated cases.
- Meningitis: When other treatments are not appropriate, especially in case of MRSA-related central nervous system infections.
- Enterocolitis: Caused by Clostridioides difficile, particularly in severe cases or when other treatments aren’t tolerated.
Empirical Vs. Targeted Therapy
| Empirical Therapy | Targeted Therapy |
|---|---|
| Vancomycin is often initiated as an empirical therapy when there’s a suspicion of a severe gram-positive infection, particularly in critical settings where the risk of MRSA is high. Here, clinicians need to act swiftly to outpace the infection. | With targeted therapy, Vancomycin administration is adjusted based on culture results and susceptibility data, ensuring the most effective and appropriate treatment. This approach reduces the risk of resistance and side effects and ensures a higher chance of infection clearance. |
Assessing Vancomycin’s Antibiotic Power
Vancomycin stands as a bastion in the world of antibiotics, often reserved for combating stubborn infections that resist other treatments. Recognized as a broad-spectrum antibiotic, it flexes its muscle against a range of Gram-positive bacteria, making it a critical player in the medical toolbox. But what defines the potency of an antibiotic like Vancomycin? Understanding its effectiveness, resistance patterns, and how it measures up to other broad-spectrum antibiotics is crucial for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Measures Of Antibiotic Effectiveness
Evaluating the effectiveness of Vancomycin hinges on several key metrics:
- Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC): This is the lowest concentration of an antibiotic that will inhibit the visible growth of a bacterium after 24 hours. A lower MIC value signifies higher potency against the targeted organism.
- Spectrum of Activity: Vancomycin is particularly potent against gram-positive bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus, and Enterococcus species, among others.
- Bactericidal vs. Bacteriostatic: Vancomycin is bactericidal, meaning it kills bacteria rather than merely inhibiting their growth.
Resistance Patterns And Concerns
Alarmingly, antibiotic resistance is on the rise, and Vancomycin is no exception to this trend. The emergence of Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci (VRE) and strains of Staphylococcus that exhibit reduced susceptibility to this antibiotic ring alarms. The clinical implications are significant, necessitating vigilant monitoring of resistance patterns and the judicious use of Vancomycin to preserve its efficacy.
Comparison With Other Broad Spectrum Antibiotics
While Vancomycin is a critical tool, it is essential to compare its power with other broad spectrum antibiotics:
| Antibiotic | Class | Spectrum | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vancomycin | Glycopeptide | Gram-positive bacteria | Severe infections like MRSA, complicated skin infections |
| Meropenem | Carbapenem | Gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria | Complicated body cavity and connective tissue infections |
| Linezolid | Oxazolidinone | Gram-positive bacteria | Resistant tuberculosis, VRE infections |
Each antibiotic provides a unique balance of breadth and potency. Vancomycin often becomes the antibiotic of choice when other therapies fail or when dealing with multidrug-resistant organisms.
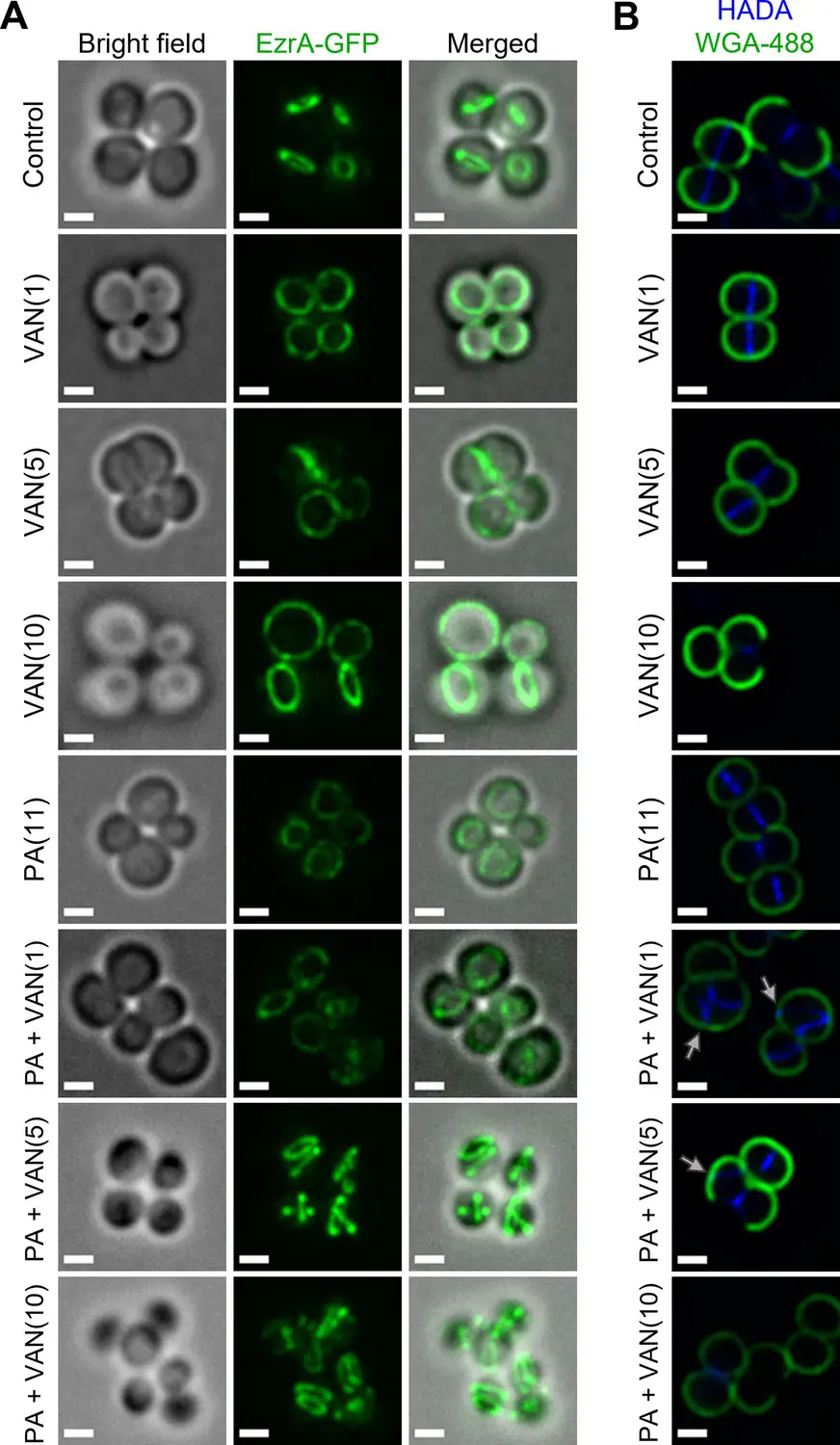
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of Is Vancomycin Broad Spectrum
What Is Vancomycin Used To Treat?
Vancomycin is a powerful antibiotic used to treat serious bacterial infections, particularly those caused by Gram-positive bacteria. It’s often prescribed for MRSA, sepsis, and infections of the bones, joints, heart, and bloodstream.
Is Vancomycin A Broad Or Narrow Spectrum Antibiotic?
Vancomycin is considered a broad-spectrum antibiotic. However, it’s primarily effective against Gram-positive bacteria, not Gram-negative bacteria. It’s reserved for severe infections when other antibiotics are ineffective.
How Does Vancomycin Work Against Bacteria?
Vancomycin works by inhibiting cell wall synthesis of bacteria, leading to cell death. It binds to bacterial cell walls, blocking the integration of new cell wall material, effectively stopping bacterial growth and multiplication.
What Are The Side Effects Of Vancomycin?
Common side effects of vancomycin include nausea, redness and rashes (often called “red man syndrome”), fever, and chills. In some cases, it can also lead to kidney toxicity or ototoxicity, especially when not properly monitored.
Conclusion
Understanding vancomycin’s role as an antibiotic clarifies its significance in treating complex infections. It stands out for its effectiveness against resistant bacteria. This characteristic makes it invaluable in specific medical scenarios. Remember, while powerful, vancomycin’s use requires careful monitoring to avoid resistance.
Consult your healthcare professional for tailored advice.