Yes, Streptomycin is a broad spectrum antibiotic effective against a wide range of bacteria causing various infections. It can treat tuberculosis, plague, tularemia, and other bacterial infections across different organ systems.
Streptomycin works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, thus preventing their growth and reproduction. This antibiotic is particularly important in treating multidrug-resistant tuberculosis and has saved numerous lives since its discovery in 1943. Streptomycin’s efficacy and versatility make it a valuable tool in modern medicine, playing a crucial role in combating bacterial infections worldwide.
Streptomycin’s Antibiotic Classification
Streptomycin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, is a potent medication that has played a crucial role in combating various bacterial infections. Understanding its antibiotic classification, specifically in relation to categorization criteria and its place among other antibiotics, is essential in appreciating its therapeutic value.
Understanding The Definition Of Broad Spectrum Antibiotics
Broad spectrum antibiotics are medications that target a wide range of bacterial species, including both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Unlike narrow-spectrum antibiotics, which are effective against specific types of bacteria, broad-spectrum antibiotics can address a broader array of bacterial infections.
Classification Criteria And Streptomycin’s Place Among Antibiotics
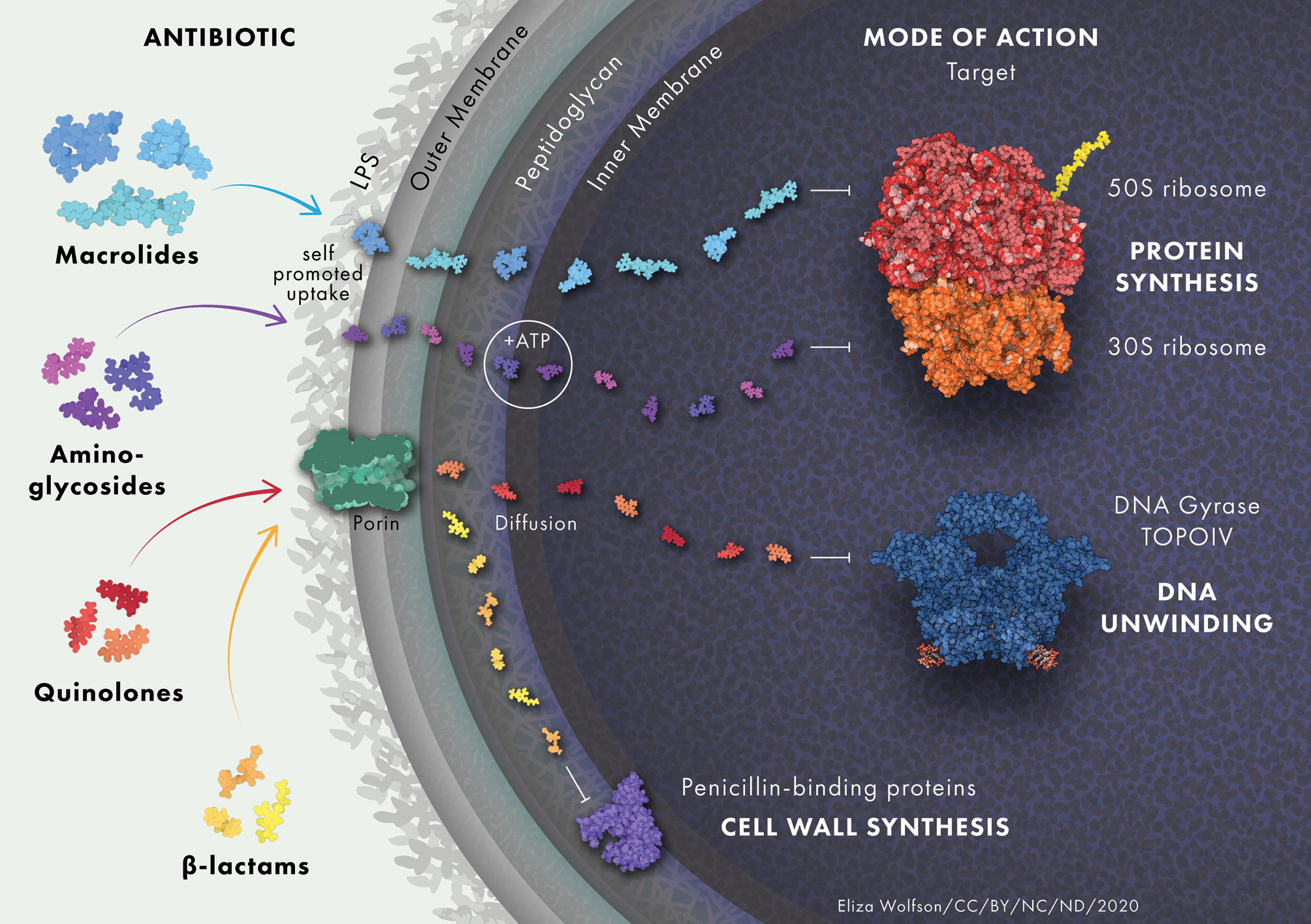
When considering antibiotic classification, factors such as the spectrum of bacterial coverage, mechanisms of action, and potential side effects play a pivotal role. Streptomycin, classified as an aminoglycoside antibiotic, has a broad spectrum of activity, making it effective against various bacterial infections. It inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit, thus disrupting the formation of the translation complex and leading to bactericidal effects.
Credit: www.frontiersin.org
Is Streptomycin Broad Spectrum
Exploring The Specific Organisms Streptomycin Targets
Streptomycin is an antibiotic that exhibits a broad spectrum of activity against various bacteria. Its primary action is to inhibit protein synthesis in bacterial cells. Specifically, streptomycin targets the following organisms:
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Streptomycin is an essential component of the treatment for drug-sensitive tuberculosis.
- Escherichia coli (E. coli): Streptomycin is effective against certain strains of E. coli, making it valuable in the treatment of urinary tract infections and other related conditions.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa: This bacterium, known for causing infections in hospitals and healthcare settings, is susceptible to the action of streptomycin.
- Salmonella: Streptomycin has been used to combat infections caused by various Salmonella species, including those responsible for foodborne illnesses.
Comparing Streptomycin’s Action To Other Antibiotics
When compared to other antibiotics, streptomycin’s mechanism of action sets it apart. While many antibiotics target specific components of bacterial cells, streptomycin’s ability to inhibit protein synthesis makes it an effective choice for combating a wide range of bacterial infections. Additionally, its ability to penetrate bacterial cells effectively gives it an advantage over some other antibiotics, making it valuable in the treatment of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial infections.
Streptomycin’s Spectrum Of Action
Understanding the spectrum of action of streptomycin is crucial in determining its effectiveness in treating various bacterial infections. Streptomycin, a well-known antibiotic, is often recognized for its broad-spectrum activity against a wide range of bacteria. Below we delve into a detailed analysis of the bacteria susceptible to streptomycin and explore the diseases and infections commonly treated with this potent antibiotic.
Detailed Analysis Of The Bacteria Susceptible To Streptomycin
Streptomycin effectively targets and inhibits the growth of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It primarily acts by disrupting protein synthesis in bacterial cells, thereby exerting bactericidal effects. The table below outlines some of the key bacteria susceptible to streptomycin:
| Bacteria Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Gram-positive | Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae |
| Gram-negative | Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
Diseases And Infections Commonly Treated With Streptomycin
Streptomycin plays a pivotal role in the treatment of various infectious diseases, particularly those caused by susceptible bacterial strains. Some of the prevalent diseases and infections effectively managed with streptomycin include:
- Tuberculosis
- Brucellosis
- Tularemia
- Bubonic plague
- Typhoid fever
By understanding the spectrum of action of streptomycin and its applications in treating specific diseases, healthcare professionals can optimize its use to combat infectious bacterial conditions effectively.
Uncovering Streptomycin’s Versatility
Investigating The Range Of Streptomycin’s Effectiveness
Streptomycin, a member of the aminoglycoside class of antibiotics, is renowned for its broad-spectrum effectiveness against a wide array of bacterial infections. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting protein synthesis in susceptible bacteria, delivering a potent antimicrobial effect.
Whether combating tuberculosis, urinary tract infections, or plague, streptomycin showcases remarkable versatility in targeting various bacterial strains. It exhibits proficiency in addressing both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, making it an invaluable asset in the medical armamentarium against infectious diseases.
Situations Where Streptomycin Is The Preferred Antibiotic Choice
Streptomycin’s efficacy particularly shines in scenarios where the infecting pathogen proves to be resistant to other antibiotic classes. Additionally, in cases of tuberculosis, especially when multi-drug resistance is a concern, streptomycin stands out as a pivotal therapeutic option.
The antibiotic’s ability to penetrate tissue barriers and reach site-specific infections, such as in the central nervous system, further underscores its significance as a preferred choice in challenging clinical conditions.
Limitations And Resistance Issues
While streptomycin is widely recognized as a broad spectrum antibiotic, it is not without limitations and faces resistance issues. Understanding these factors is crucial in the ongoing battle against antibiotic resistance.
Factors Contributing To The Development Of Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance can emerge due to several factors, including:
- Overuse and misuse of antibiotics
- Incomplete treatment courses
- Use of antibiotics in agriculture
- Horizontal gene transfer among bacteria
- Evolution of bacterial strains
Streptomycin’s Efficacy In The Face Of Emerging Resistant Strains
While streptomycin has historically been effective against a wide range of bacteria, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other Gram-negative organisms, it has also encountered challenges from emerging resistant strains. Factors influencing its efficacy include:
- Mechanisms of action and resistance
- Cross-resistance with other antibiotics
- Developing alternative treatment strategies
Tailoring Treatment With Streptomycin
When it comes to tailoring treatment with streptomycin, it is crucial to understand its impact as a broad-spectrum antibiotic and the decision-making process for using it in clinical practice. Streptomycin, a potent antibiotic, is known for its efficacy in treating a wide range of bacterial infections. Its unique mechanism of action makes it a valuable tool in combating various pathogens, allowing for tailored treatment in specific medical scenarios.
Decision-making Process For Using Streptomycin In Clinical Practice
Utilizing streptomycin in clinical practice involves a meticulous decision-making process to ensure its effectiveness and minimize potential resistance. Healthcare professionals assess several factors before incorporating streptomycin into a treatment regimen:
- Identification of the specific bacterial strain causing the infection
- Evaluation of the infection’s severity and location
- Assessment of the patient’s medical history and potential allergic reactions
- Considering any existing resistance patterns in the local community
Case Studies Reflecting Streptomycin’s Successful Application In Medical Treatments
Several case studies demonstrate streptomycin’s successful application in treating various medical conditions, showcasing its versatility and efficacy in tailored treatment:
- Case Study 1: Treatment of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection with streptomycin, leading to successful eradication of the pathogen.
- Case Study 2: Management of severe Salmonella infection using streptomycin, resulting in a rapid clinical improvement and resolution of symptoms.
- Case Study 3: Successful treatment of Yersinia pestis infection, highlighting streptomycin’s effectiveness in combating potential bioterrorism threats.
Frequently Asked Questions Of Is Streptomycin A Broad Spectrum Antibiotic
What Is Streptomycin And How Does It Work?
Streptomycin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria, making it effective against a wide range of bacterial infections. It works by binding to the bacterial ribosome and disrupting protein production, ultimately leading to bacterial cell death.
What Bacterial Infections Does Streptomycin Treat?
Streptomycin is commonly used to treat tuberculosis, as well as other bacterial infections such as plague, tularemia, and certain types of brucellosis. It is particularly effective against bacterial strains that have developed resistance to other antibiotics.
Are There Any Side Effects Associated With Streptomycin Usage?
Yes, some potential side effects of streptomycin usage include ototoxicity (damage to the ears), nephrotoxicity (kidney damage), and allergic reactions. It’s important to use this antibiotic only as prescribed by a healthcare professional and to be aware of any potential adverse effects.
Can Streptomycin Be Used For Both Adults And Children?
Streptomycin can be used in both adults and children, but dosage and administration may vary based on age, weight, and the specific condition being treated. It’s crucial to follow the guidance of a healthcare provider when using streptomycin, especially in pediatric populations.
Conclusion
Streptomycin demonstrates broad-spectrum antibiotic activity against a wide range of bacteria. Its ability to target both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria makes it a valuable weapon in the fight against infections. With further research and development, Streptomycin’s potential to combat various bacterial diseases will continue to be explored and harnessed.